Difference Between Traditional SEO and GEO: 2026 Analysis
The Evolution of Search Visibility
In my years as an SEO consultant, I have watched the search landscape shift from simple keyword matching to complex semantic understanding. But nothing has disrupted our industry quite like the emergence of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). If you are a business owner or marketing manager today, understanding the difference between traditional seo and geo is no longer optional—it is the baseline for survival in a digital-first economy.
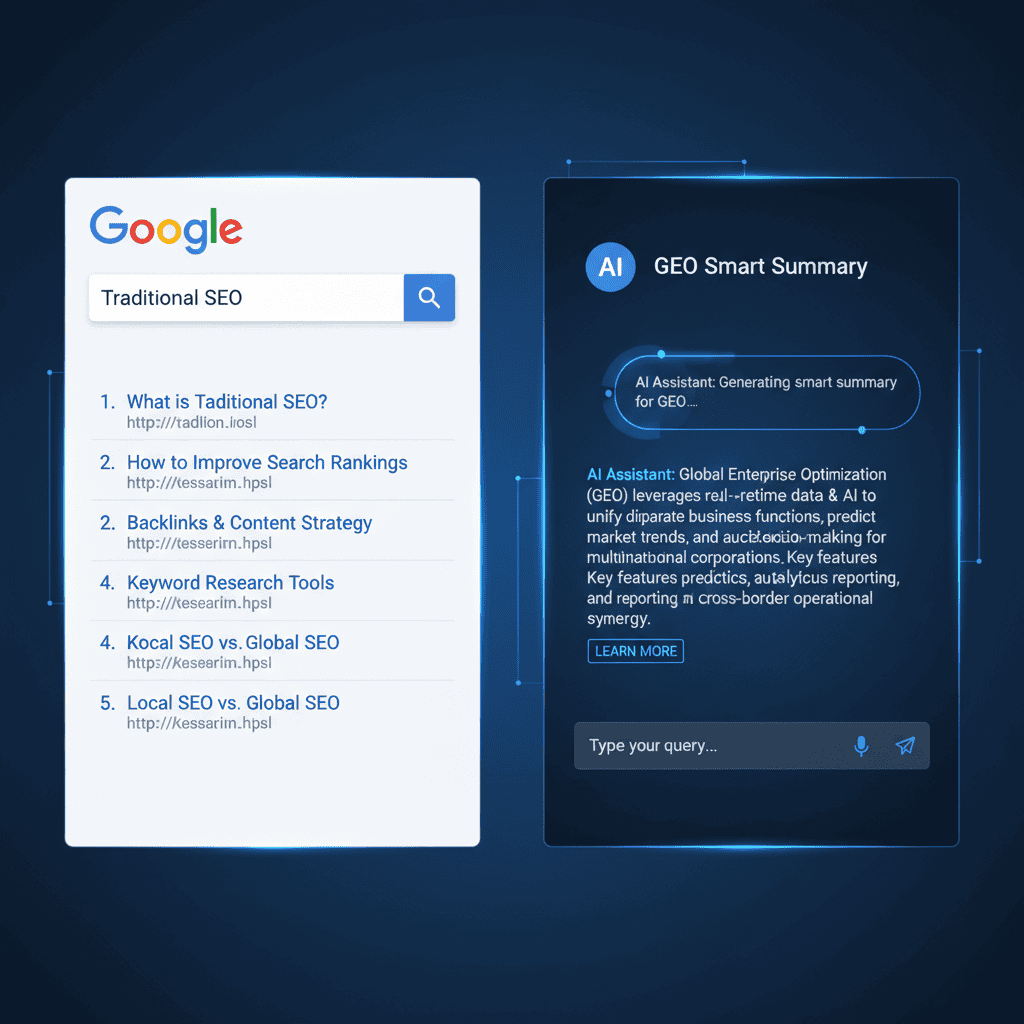
While traditional SEO focuses on helping search engines like Google find and rank your website to drive traffic, GEO is a fundamentally different game. It focuses on helping AI models (like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Google’s AI Overviews) understand and cite your content as a factual authority. The goal has shifted from “getting the click” to “being the answer.”
Key Takeaways
• Goal Shift: SEO targets SERP rankings; GEO targets AI citations and mentions.
• Measurement: SEO relies on traffic and conversions; GEO relies on brand visibility and citation frequency.
• Tactics: SEO prioritizes keywords and backlinks; GEO prioritizes structured data and entity authority.
Core Differences: Goals and Mechanics
To truly grasp the difference between traditional SEO and GEO, we must look at what happens under the hood. Traditional SEO is built on the concept of retrieval. A user types a query, and the engine retrieves a list of documents (web pages) ranked by relevance and authority (PageRank).
GEO, however, operates on synthesis. The AI engine does not just retrieve a list; it reads multiple sources, extracts facts, and synthesizes a singular answer. This means your content needs to be optimized for machine readability, not just human readability.
Comparison of Objectives
The following table outlines the fundamental strategic shifts required when moving from a pure SEO mindset to a hybrid GEO approach.
| Feature | Traditional SEO | Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank #1 on SERP to drive clicks to the site. | Be cited as a source in the AI-generated answer. |
| User Journey | Search -> Click -> Consume Content. | Search -> Read AI Answer -> (Optional) Click Citation. |
| Key Metric | Organic Traffic, CTR, Keyword Rankings. | Citation Frequency, Share of Voice, Brand Mentions. |
| Content Focus | Comprehensive guides, long-form content. | Fact-dense snippets, direct answers, data tables. |
| Technical Basis | Crawlability, Page Speed, Core Web Vitals. | Entity Relationships, Schema Markup, Contextual Vector. |
The Shift in Crawler Behavior
In traditional SEO, Googlebot crawls your site to index pages. If your page is slow or has broken links, you lose rankings. In GEO, AI models act more like “fact extractors.” They are looking for specific, verifiable entities (names, prices, dates) that they can use to construct an answer.
According to a comprehensive comparison of AI search, AI crawlers selectively extract facts for model training rather than indexing the entire site structure. This means a technically perfect site with vague content might rank well in SEO but fail in GEO because the AI cannot extract a definitive answer.
Content Strategy: Keywords vs. Entities
The biggest practical difference lies in how we write content. For the last decade, we optimized for keywords. If I wanted to rank for “best CRM software,” I would write a 2,000-word guide using that phrase repeatedly.
In the GEO era, keywords are secondary to entities. An entity is a distinct concept (a person, place, thing, or idea) that the AI understands. To succeed in GEO, you must define the relationships between entities clearly.
Structuring for the Machine
Research from the University of Pennsylvania suggests that simple formatting changes can have a massive impact on GEO performance. They found that using bullet lists can increase citation rates by 30-40% in generative engines. This is because lists are easier for Large Language Models (LLMs) to parse and verify.
Strategic Adjustments for Content:
- Direct Answers: Start your paragraphs with the answer, then explain. AI models prefer “inverted pyramid” writing.
- Structured Data: Use Schema.org markup heavily. This is the language of entities.
- Fact Density: Increase the number of unique facts per paragraph. Fluff is ignored by AI.
This shift is particularly relevant when deciding between local SEO vs national SEO. Local queries are often answered directly by AI (e.g., “best pizza near me”), making entity optimization for your business name and location critical.
Measuring Success in a Zero-Click World
One of the most daunting aspects of GEO is the measurement challenge. In traditional SEO, I can log into Google Search Console and see exactly how many clicks a keyword drove. In GEO, the user might get their answer without ever visiting your site. This is the “Zero-Click” phenomenon.
However, this doesn’t mean GEO is valueless. It changes the value proposition from traffic to brand authority. Being cited by an AI engine signals to the user that your brand is a trusted source.
Metrics That Matter Now
• Citation Frequency: How often is your brand mentioned in AI summaries?
• Sentiment Analysis: Is the AI describing your brand positively?
• Entity Salience: How strongly is your brand associated with your core topics?
Data from 2024 indicates that 65% of marketers are already adapting strategies for AI-generated results. This aligns with optimizing for generative engines, where the focus is on influencing the output rather than just ranking the input.
Why You Need Both Strategies
Does GEO replace traditional SEO? Absolutely not. They are complementary. Traditional SEO ensures you capture users who want deep dives, transactional experiences, or specific website functionality. GEO ensures you remain visible for informational queries where users want quick answers.
For professional services, this hybrid approach is vital. As I discussed in my analysis of the future of SEO for professional firms, trust signals are the currency of the future. SEO builds the infrastructure of trust (technical site health), while GEO builds the reputation of trust (citations and answers).
The Hybrid Workflow
To maximize results, I recommend a workflow that integrates both:
- Create the Foundation: Build a technically sound site (SEO).
- Optimize for Depth: Write comprehensive articles that cover the topic fully (SEO).
- Optimize for Extraction: Add summary tables, FAQs, and schema markup to that same content (GEO).
- Build Authority: Focus on Digital PR and citations to establish your entity (GEO).
This approach ensures you don’t lose your existing organic traffic while positioning yourself for the AI-driven future described in content strategy shifts.
Practical Application: A Real-World Example
Let’s look at a “Roof Replacement Cost” query to see the difference in action.
Traditional SEO Approach:
• Create a blog post titled “Complete Guide to Roof Replacement Costs in 2026.”
• Use the keyword 15 times.
• Include long paragraphs explaining variables like material and labor.
• Result: User clicks, reads for 2 minutes, maybe calls.
GEO Approach:
• Create the same blog post.
• Add a data table at the top: “Average Cost by Material: Asphalt ($5k), Metal ($12k).”
• Use FAQ Schema to mark up specific questions.
• Result: AI Overview displays your pricing table and cites your brand. User sees you as the authority immediately.
This is how you build your personal brand with AI—by becoming the undeniable source of truth that the machines rely on.
FAQ Section
What is the main difference between SEO and GEO?
Traditional SEO optimizes content to rank in search engine results pages (SERPs) to drive clicks. GEO optimizes content to be understood and synthesized by AI models to generate direct answers and citations.
Will GEO replace traditional SEO?
No. GEO is an evolution, not a replacement. While AI answers many informational queries, users still need websites for transactions, deep research, and complex services. A balanced strategy requires both.
How do I optimize for GEO?
Focus on structured data (Schema.org), high fact density, direct answers, and skimmable formats like bullet points and tables. Ensure your brand is clearly defined as an entity across the web.
Can I track GEO results like SEO traffic?
It is more difficult. You cannot track “clicks” from zero-click answers easily. Instead, you must measure share of voice, brand mentions, and citation frequency in AI responses.
Conclusion
The difference between traditional SEO and GEO ultimately comes down to who you are trying to impress. SEO impresses the algorithm’s indexer; GEO impresses the AI’s synthesizer. In 2026, the most successful businesses will be those that speak the language of both.
Don’t abandon your SEO roots—technical health and backlinks still matter. But start layering in the structured, fact-based signals that GEO demands. By doing so, you future-proof your visibility against the rising tide of generative search.